Proposed Network Design Solutions
Solving Business Requirements
| Business Requirement & Reason | Solution & Explanation |
|---|---|
| Data Storage System Needed to securely store and manage company data. |
Ubuntu Server — A reliable and secure system to store and manage company data. |
| Backup Internet Connection Ensure internet stays online even if the main line fails. |
VRRP on Router — Automatically switches to backup internet if the main one fails, ensuring constant connectivity. |
| Device Failure Recovery Keep network running smoothly even when hardware fails. |
HSRP — Quickly switches to a backup device if the primary one stops working. |
| Separate Departments Keep different departments' network traffic separated for security and efficiency. |
VLAN & VTP — Organizes network traffic by department to improve security and reduce interference. |
| Company Website Hosting Provide a reliable platform to publish the company website. |
Apache 2 Webservice — Hosts the company website to make it accessible to users. |
| Network Monitoring Detect and respond to network issues quickly. |
Syslog & SNMP — Tools to monitor network activity and alert administrators of problems. |
| Internal Security Prevent unauthorized access to the company network. |
Port Security — Blocks unauthorized devices from connecting to network ports. |
| Remote Work Support Enable employees to securely work from outside the office. |
VPN — Provides secure remote access to the company network. |
| Email & Virus Protection Protect company email and network from malware and attacks. |
Fortinet Firewall — Guards against viruses and unauthorized access through email and network traffic. |
| Reduce Network Traffic Congestion Improve network speed and reliability during heavy use. |
Etherchannel & Load Balancing — Combines multiple network connections for faster and more reliable data transfer. |
Network Topology
Network System Diagram
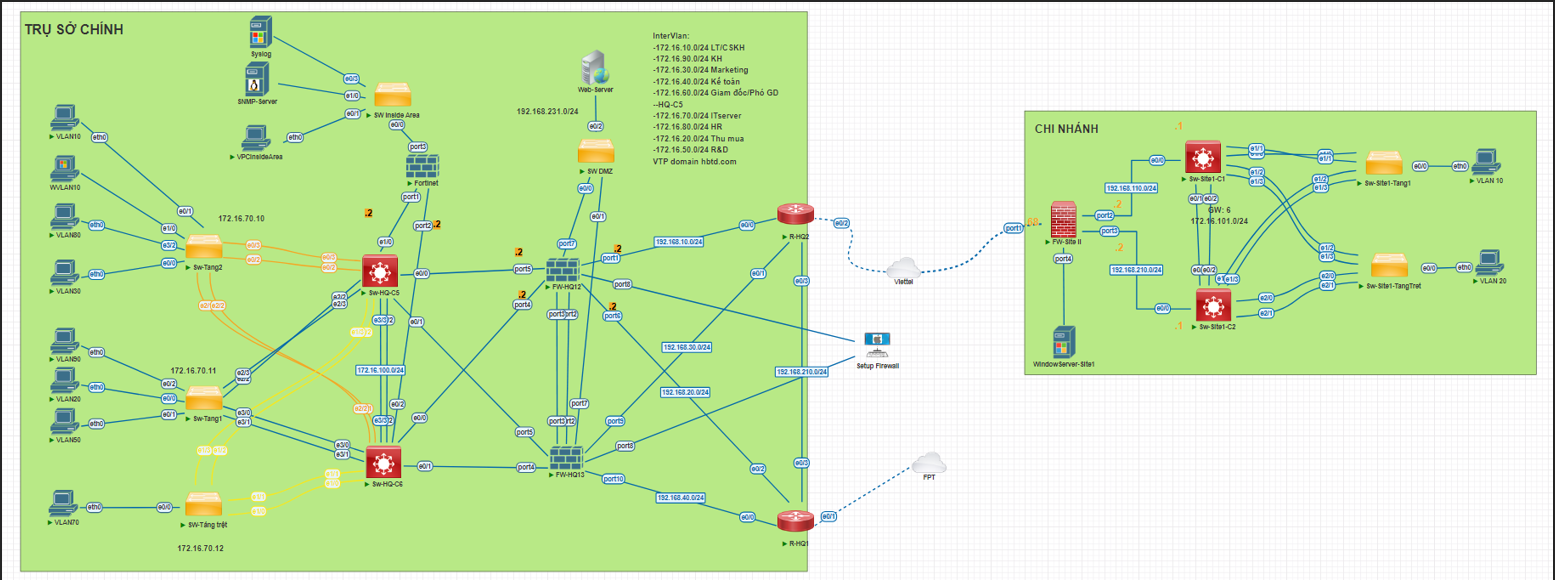
Network Infrastructure Technologies and Protocols
HSRP (Hot Standby Router Protocol)
HSRP ensures continuous network availability by allowing multiple routers to work together. If the main router fails, another router automatically takes over without interrupting network access.
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First)
OSPF is a routing protocol that helps routers efficiently find the fastest path to send data across a network, improving speed and reliability.
NAT (Network Address Translation)
NAT translates private IP addresses used inside the company to public IP addresses used on the internet. This helps conserve public IPs and adds a layer of security by hiding internal network details.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol)
DHCP automatically assigns IP addresses to devices when they connect to the network, simplifying setup and management.
VTP (VLAN Trunking Protocol)
VTP manages VLAN configurations across multiple network switches, ensuring that all devices in the same VLAN can communicate regardless of which switch they connect to.
EtherChannel
EtherChannel bundles several physical network connections into a single logical link, increasing bandwidth and providing redundancy if one connection fails.
VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network)
VLANs divide a physical network into multiple logical networks. This segmentation improves security, reduces congestion, and helps organize departments or user groups.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
|
Weaknesses
|
Opportunities
|
Threats
|